Multi-sensory extended reality (XR) is a term that encompasses various technologies that create immersive and interactive digital experiences that stimulate multiple senses, such as sight, sound, touch, smell, and taste. Multi-sensory XR can be used for various purposes, such as entertainment, education, health, tourism, and social interaction.
Multi-sensory XR is important because it can enhance our quality of life, well-being, and happiness by allowing us to relive our cherished memories, experience new places and cultures, and connect with others in more meaningful ways. Multi-sensory XR can also help us cope with stress, anxiety, loneliness, and trauma by providing us with positive and soothing stimuli.
How 6G will enable multi-sensory XR
6G is the next generation of wireless communication technology that is expected to be available by 2030. 6G will offer unprecedented speed, capacity, reliability, and intelligence, enabling new applications and services that are beyond the capabilities of 5G.
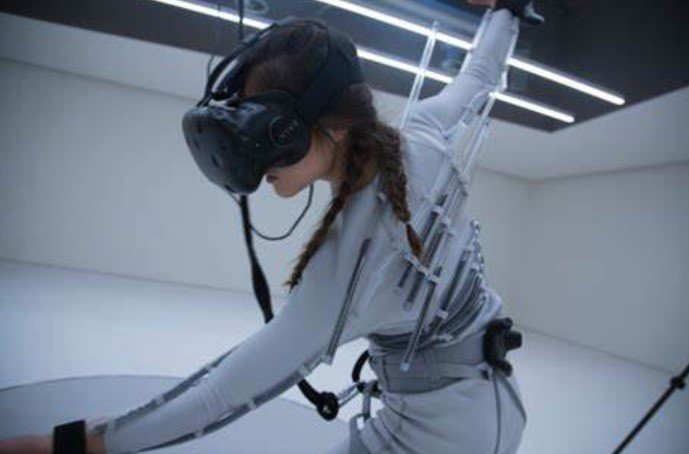

One of the key features of 6G is that it will enable multi-sensory XR by providing the necessary bandwidth, latency, and computing power to transmit and process large amounts of sensory data in real time. 6G will also leverage artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and cloud computing to create realistic and personalized multi-sensory XR content that can adapt to the user’s preferences, context, and emotions.
What are some examples of multi-sensory XR applications powered by 6G?
At the Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2024 in Barcelona, Spain, several companies and organizations showcased their multi-sensory XR applications powered by 6G. Some of the examples are:
- NTT, a Japanese telecoms company, demonstrated its ‘Feel Tech’ project, which aims to recreate multi-sense experiences and memories from across the world. Using 6G, NTT can capture, store, and reproduce sensory information, such as temperature, humidity, wind, smell, and taste, and deliver it to the user through wearable devices, such as glasses, headphones, gloves, and vests. For instance, a user can relive their happiest memory of visiting a tropical island by wearing the ‘Feel Tech’ devices and experiencing the same sensory stimuli as they did in the past.
- Ericsson, a Swedish telecoms company, and Turkcell, a Turkish telecoms company, signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) at MWC 2024 to advance 6G research and development and drive technological advancements in Türkiye. One of their main focus areas is multi-sensory XR, especially in the fields of AI, ML, and overall 6G vision and architecture. Ericsson and Turkcell aim to pioneer the groundwork for innovative future use cases, such as immersive education, telemedicine, and social VR.
- Next G Alliance, a North American initiative that aims to advance global leadership in 6G and beyond, published a white paper on multi-sensory XR in 6G. The paper identifies the promise of multi-sensory XR, surveys the current state of the technology and its evolution from 5G, and identifies requirements to advance XR applications, such as standardization, interoperability, security, and privacy. The paper also suggests potential research areas, such as haptic feedback, olfactory display, and brain-computer interface.
What are the challenges and opportunities of multi-sensory XR powered by 6G?
Multi-sensory XR powered by 6G is a promising and exciting technology that can revolutionize various domains and industries. However, it also poses some challenges and opportunities that need to be addressed and explored. Some of them are:
- Ethical and social implications: Multi-sensory XR can have positive and negative impacts on the user’s psychology, behavior, and well-being. For example, multi-sensory XR can help users cope with stress, but it can also cause addiction, isolation, or detachment from reality. Multi-sensory XR can also raise ethical and social issues, such as consent, privacy, ownership, and authenticity of sensory data and content. Therefore, multi-sensory XR needs to be designed and regulated with ethical and social considerations in mind, and users need to be educated and informed about the potential risks and benefits of using multi-sensory XR.
- Technical and operational challenges: Multi-sensory XR requires high-performance and reliable infrastructure, devices, and networks to support the transmission and processing of large amounts of sensory data in real time. Multi-sensory XR also requires sophisticated and robust algorithms and models to create realistic and personalized multi-sensory XR content that can adapt to the user’s preferences, context, and emotions. Therefore, multi-sensory XR needs to overcome technical and operational challenges, such as scalability, compatibility, quality, and security of multi-sensory XR systems and services.
- Innovation and collaboration opportunities: Multi-sensory XR offers a vast and diverse range of applications and services that can benefit various domains and industries, such as entertainment, education, health, tourism, and social interaction. Multi-sensory XR also offers a unique and novel way of experiencing and interacting with the digital and physical world, creating new possibilities and opportunities for innovation and creativity. Therefore, multi-sensory XR needs to foster innovation and collaboration opportunities among various stakeholders, such as researchers, developers, providers, users, and regulators, to explore and exploit the full potential of multi-sensory XR.