In an age where convenience often trumps quality, a recent study has shed light on the potential dangers of ultra-processed foods, linking them to an increased risk of glaucoma. This eye-opening research emphasizes the importance of dietary choices and their implications for ocular health.
The Study’s Findings
The study, conducted among Spanish university graduates, revealed a significant correlation between high consumption of ultra-processed foods and the development of glaucoma. Participants who indulged in more than four servings per day were found to have an 80% higher risk of this eye condition compared to those who consumed less. These findings underscore the need for a closer examination of our eating habits and their long-term effects on our health.
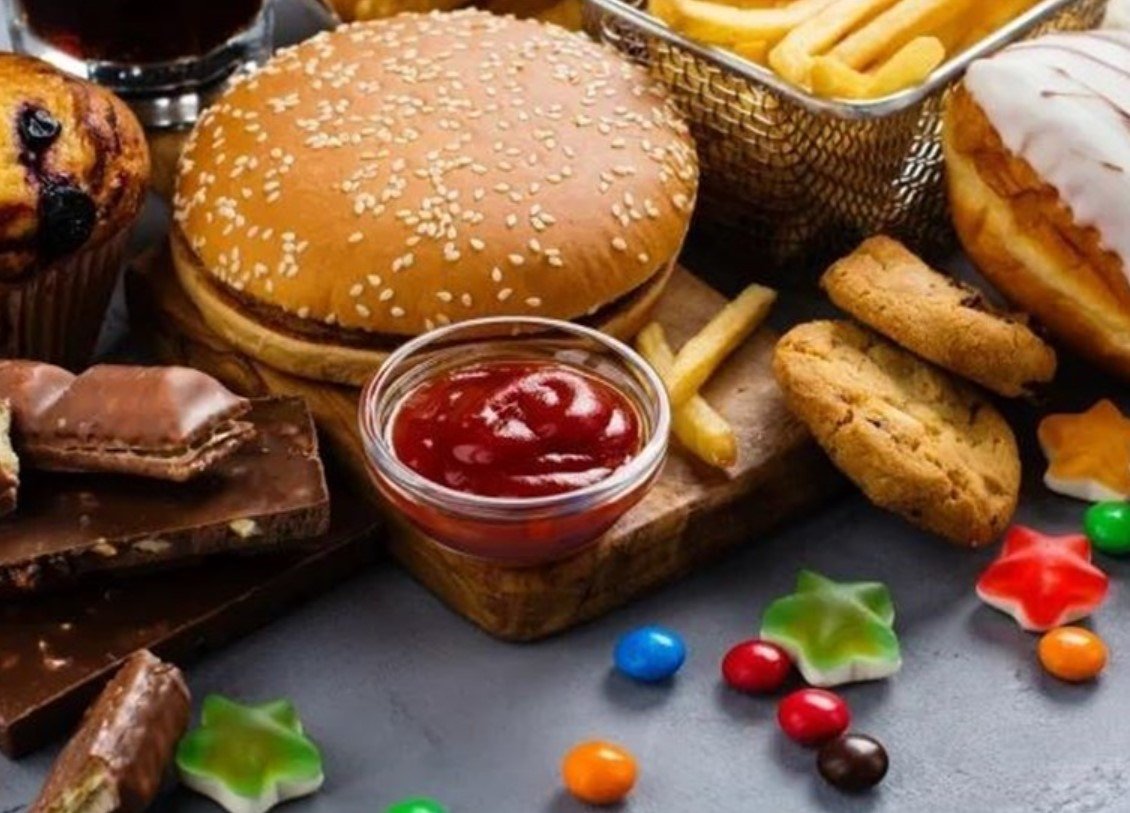

The research highlighted the role of sweets, particularly ultra-processed ones, in elevating the risk of glaucoma. It suggests that the high levels of sugar, salt, and fat present in these foods may be contributing factors. The study’s results are a call to action for individuals to reassess their diets and consider the impact of their food choices on their overall well-being.
Implications for Public Health
The implications of this study are far-reaching, with potential impacts on public health policies and dietary guidelines. As glaucoma remains a leading cause of blindness, understanding the environmental and lifestyle factors that contribute to its development is crucial. This research adds to the growing body of evidence that points to the importance of diet in preventing chronic diseases.
The study’s findings could influence future recommendations on food consumption, particularly regarding ultra-processed foods. It also highlights the need for further research to explore the mechanisms behind the association between diet and glaucoma risk. As we move towards a more health-conscious society, the study serves as a reminder of the power of nutrition in maintaining our health and preventing disease.
Towards a Healthier Future
In light of these findings, there is a growing movement towards healthier eating habits and a reduction in ultra-processed food intake. The study advocates for a shift in consumer behavior, encouraging individuals to opt for whole and minimally processed foods. Such changes could have a profound impact on the prevalence of glaucoma and other diet-related health issues.
Educational campaigns and initiatives that promote healthy eating could play a significant role in mitigating the risks associated with ultra-processed foods. By raising awareness of the link between diet and eye health, we can empower individuals to make informed choices that benefit their long-term health.